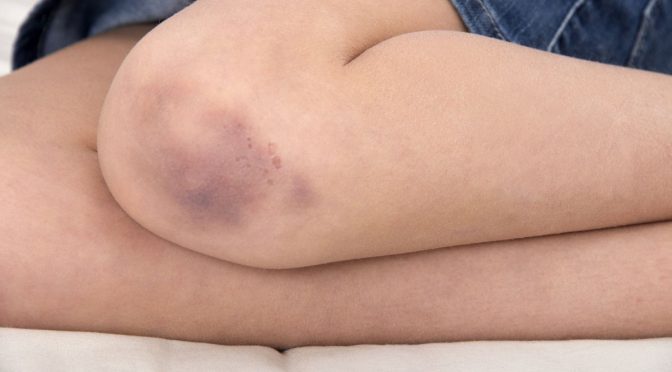
Bruising,or ecchymosis,occurs when small blood vessels called capillaries burst beneath the skin’s surface,causing blood to pool and resulting in discoloration.Although bruising can happen to anyone at any age,older adults are generally more prone to it.Physical activities like weight training can also cause minor bruising due to repetitive movements.In such cases,rest,hydration,and time usually help the injury heal.However,unexplained bruising may indicate underlying health conditions that require further medical evaluation and treatment.
1.Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy,a treatment used to combat the rapid growth of cancer cells,affects both cancerous and healthy cells in the body.One side effect is a reduced platelet count,which hampers the blood’s ability to clot,leading to easier bruising.Patients undergoing chemotherapy are advised to avoid certain medications,like over-the-counter painkillers,that can thin the blood,and to take precautions such as moisturizing chapped skin and using softer toothbrushes to prevent bleeding.
2.Cushing Syndrome
Cushing syndrome is characterized by an excess of cortisol in the body,leading to thinning skin that bruises easily.Weight gain,a common symptom of the syndrome,can exacerbate skin thinning,increasing the likelihood of hemorrhages.Proper diagnosis and treatment,often involving the removal of tumors that cause the condition,can help manage and potentially cure Cushing syndrome.However,steroid medications used to treat other conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or asthma can complicate treatment.
3.Diabetes
Diabetes,a condition that affects blood sugar levels,can also disrupt circulation,leading to nerve damage and weakened capillary walls.This makes random bruising more common,particularly in the feet.Managing blood sugar levels and regularly checking for bruises or ulcers on the feet can help mitigate these effects.
4.Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome(EDS)is a genetic disorder that affects the connective tissues of the skin,bones,and organs,making them fragile and prone to bruising and internal bleeding.People with EDS are at risk of extensive bruising and spontaneous ruptures due to the instability of their connective tissues.Treatment often involves monitoring clotting factors,managing pain,and sometimes surgery.
5.Hemophilia
Hemophilia is a genetic disorder that impairs the blood’s ability to clot,leading to frequent and sometimes severe bruising from even minor injuries.Depending on which clotting factor is missing,treatment may involve regular infusions of the missing factor,such as antihemophilic globulin for hemophilia A or plasma thromboplastin component for hemophilia B.
6.Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Lymphomas,including Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin types,are cancers that cause abnormal growth of lymphocytes,a type of white blood cell.In some cases,these abnormal cells can lead to anemia by destroying red blood cells or impairing bone marrow function,resulting in easy bruising.Treatment options include stem cell or bone marrow transplants to restore healthy blood cell production.
7.Immune Thrombocytopenia(ITP)
Immune thrombocytopenia(ITP)is a condition marked by low platelet counts,which can cause bruising even with minimal injury.The exact cause of ITP is often unclear,but it may be linked to viral or bacterial infections.Treatment typically focuses on increasing platelet counts,sometimes through medication or surgical removal of the spleen(splenectomy).
8.Thrombophilia
Thrombophilia is an inherited disorder that leads to excessive blood clotting.Unlike hemophilia,which causes too much bleeding,thrombophilia can result in dangerous blood clots.Treatment often involves anticoagulants,which,while reducing clotting,can also increase the risk of bruising.Patients may need to adjust their lifestyle to manage the condition effectively.
9.Vitamin Deficiencies
A deficiency in certain vitamins,particularly Vitamin K and Vitamin C,can lead to random bruising.Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting,while Vitamin C is crucial for maintaining the health of skin and blood vessels.Once diagnosed,these deficiencies can be treated with specialized vitamin supplements prescribed by a doctor.
10.von Willebrand Disease
Von Willebrand disease is a genetic disorder that affects the blood’s ability to clot,similar to hemophilia.It often results from low levels of von Willebrand factor,a protein necessary for platelets to stick together.Treatment depends on the subtype of the disease and may involve concentrated doses of clotting factors or synthetic hormones to control bleeding.
Understanding the potential causes of random bruising is crucial,as it can indicate serious underlying health issues.If you experience unexplained bruising,it is important to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment.